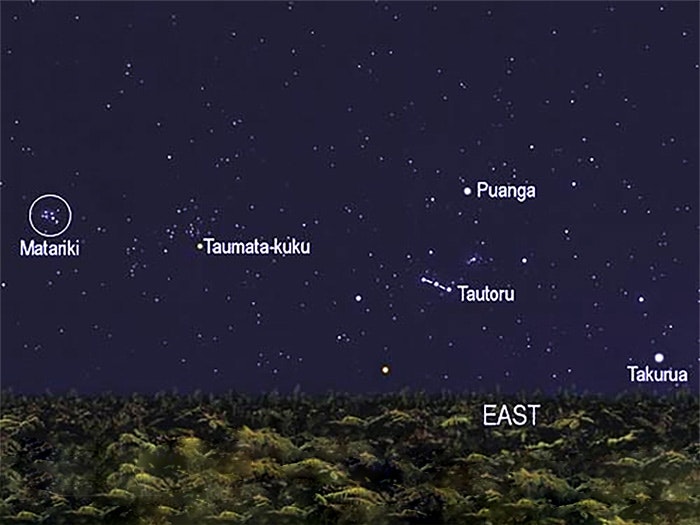
The difference between Puanga and Matariki
Some iwi celebrate Puanga rather than Matariki. Che Wilson of Whanganui iwi explains why this is the case, and which iwi celebrate Puanga.
Free museum entry for New Zealanders and people living in New Zealand
Open every day 10am-6pm
(except Christmas Day)
Free museum entry for New Zealanders and people living in New Zealand
Matariki isn’t universally observed, due to a variety of reasons – including the fact that the cluster is not visible to everyone in Aotearoa New Zealand. Learn about regional variations in marking te Mātahi o te Tau (the Māori new year).

Some iwi celebrate Puanga rather than Matariki. Che Wilson of Whanganui iwi explains why this is the case, and which iwi celebrate Puanga.

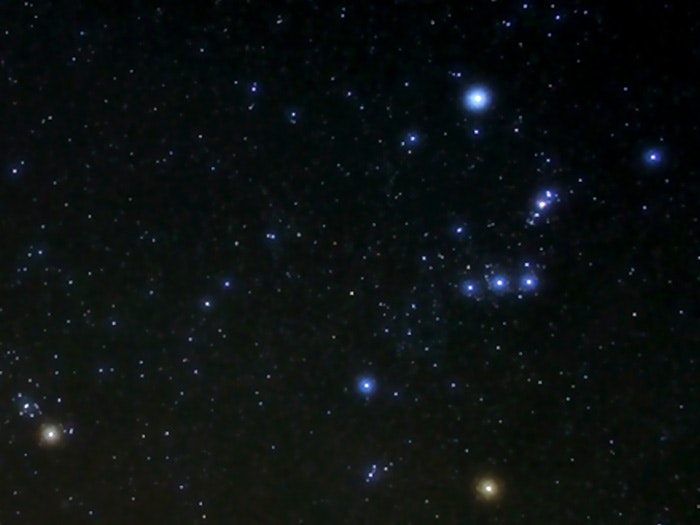
For some people the Matariki star cluster is made up of seven stars, while for others it’s nine. So which is it? Both.

Hear Te Waari Carkeek, from Ngāti Toa Rangatira iwi, tell the story of how the seven Matariki stars use their special talents and skills to help their kuia, Papatūānuku (the earth), prepare for the new year.
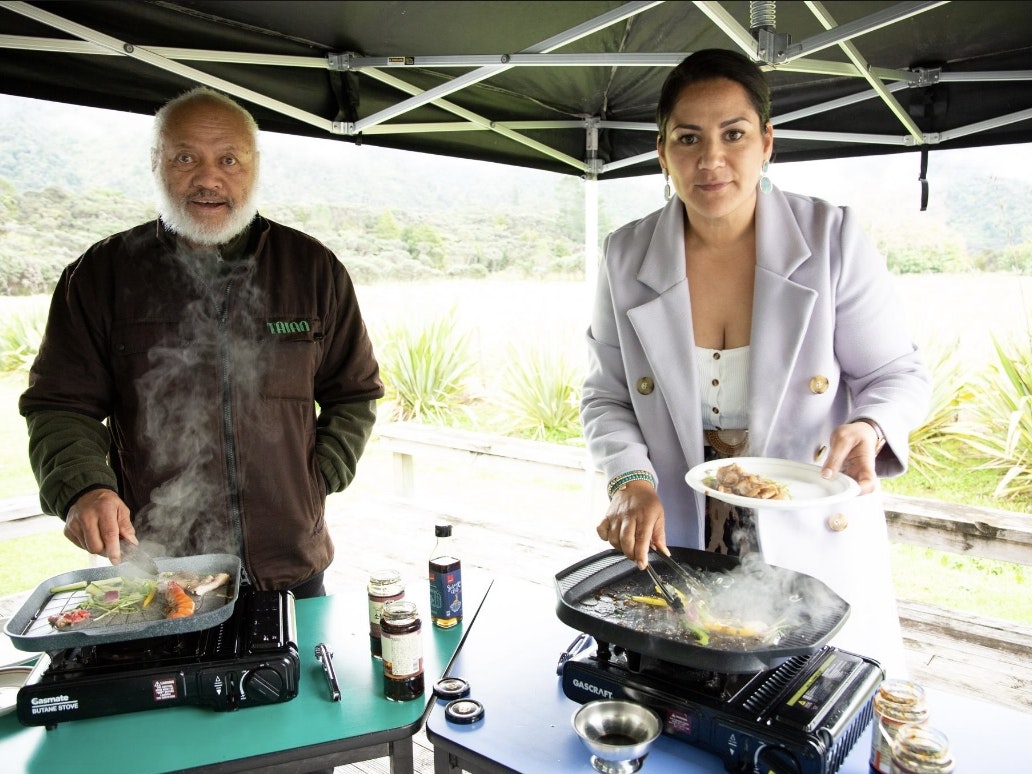

Throughout the weeks leading up to Matariki, 2024, guest speakers gave a series of talks about kai Māori practices connected to taonga (treasures) from our collection.
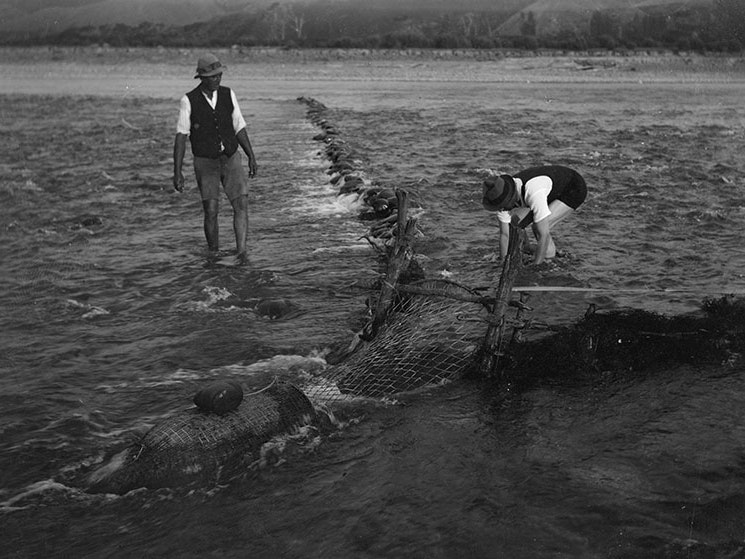
This kōrero (talk) is about Puanga – the whetū (star) that for some iwi (tribes), signals the Māori New Year.

Richard Hall, President of the Phoenix Astronomical Society, and Vice President Ian Cooper explain when we can see the star Puanga and why it’s linked to Matariki.